The Manufacturing Process and Versatility of Wire Mesh
July 9th, 2025
Key Takeaway:
- Wire mesh is valued for its strength, versatility, and cost-effectiveness in construction, industrial, and infrastructure.
- Manufacturing involves selecting raw materials, precision wire drawing, automated welding, and quality checks (ASTM standards) for durable, corrosion-resistant mesh. Sustainable practices include recycled materials, energy efficiency, and product longevity.
- Wire mesh has wide-ranging applications including concrete, architectural, safety, filtration, and infrastructure.
Wire mesh is valued for its strength, versatility, and cost-effectiveness across a wide range of applications in construction and other industries. The manufacturing process used to create the material gives it certain properties that make it a beneficial component wherever it is used.
Manufacturing Process of Wire Mesh
Raw Material Selection
High-quality wire mesh production starts with the careful selection of steel wire. Depending on the intended application, manufacturers choose from galvanized, stainless, or low-carbon steel wire to ensure the right strength, corrosion resistance, and durability needed for the project. No matter which type of steel is used, this material must adhere to industry standards to guarantee consistent and traceable properties throughout the manufacturing process.
Wire Drawing
Once the steel wire is selected, it undergoes a wire drawing process. This involves reducing the diameter of steel wire rods through rolling or cold-stretching to achieve precise specifications. The wires are then cleaned and straightened, removing impurities and ensuring uniformity before mesh formation begins.
Mesh Formation
Wire mesh manufacturing centers on creating a grid pattern with longitudinal and transverse wires placed at specific intervals. These intersecting wires are then fused using electric resistance welding, forming strong, durable joints. Automated mesh welding machines ensure consistent grid formation and high production efficiency. Strict quality controls are maintained throughout this process, enforcing adherence to ASTM and other industry standards for grid dimensions and tolerances.
Post-Production Treatments
Following mesh formation, the product undergoes trimming and straightening to eliminate excess material and achieve clean, uniform edges. To enhance corrosion resistance and extend the mesh’s service life, surface treatments such as galvanization, powder coating, or epoxy coating are then applied. Which surface treatment is used is determined by the mesh’s intended use and environmental exposure.
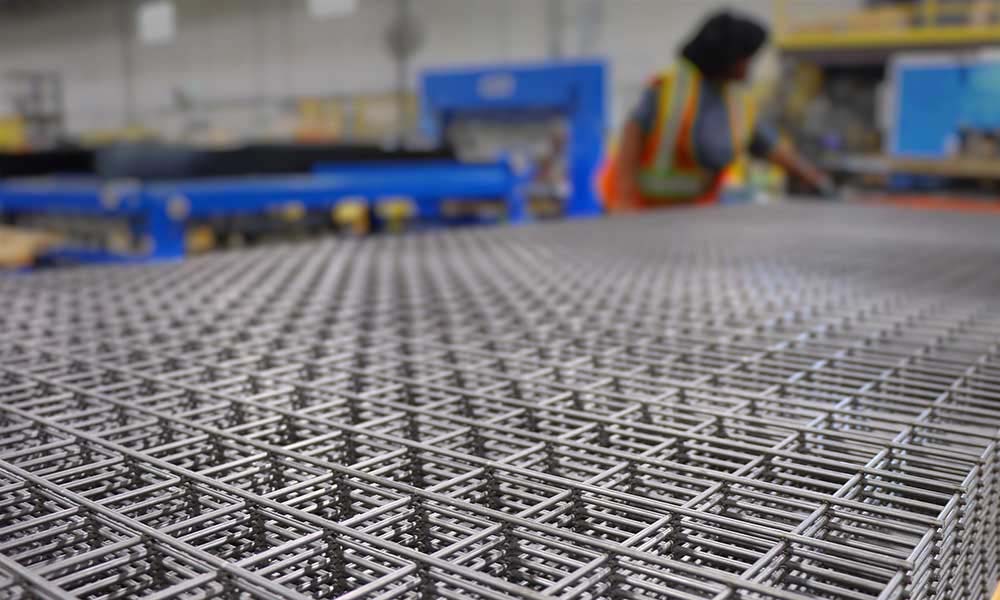

Quality Control Measures
Quality is paramount in wire mesh production. Rigorous batch testing assesses tensile strength, flexibility, and dimensional accuracy. Welding patterns are checked for consistency, and all products are verified to meet specified tolerances and standards, such as ASTM A1064. Advanced automation and sensor technology enable real-time quality monitoring, ensuring every batch meets stringent industry requirements.
Properties of Wire Mesh
Wire mesh offers several key advantages that make it indispensable across industries:
Strength and Durability: High tensile strength and robust welded joints make wire mesh suitable for demanding structural applications.
Flexibility and Versatility: Wire mesh can be customized to various shapes, sizes, and functions, serving diverse needs from construction to industrial operations.
Cost-Effectiveness: Prefabricated mesh reduces material waste, labor, and installation time compared to traditional reinforcement methods.
Corrosion Resistance: Galvanized and coated meshes provide superior resistance to rust and environmental degradation, ensuring longevity even in harsh conditions.
Lightweight Yet Sturdy: Despite its ease of handling and transport, wire mesh maintains excellent structural integrity, simplifying both logistics and installation.
Applications in Construction
In construction, wire mesh is widely used for three main purposes:
Concrete Reinforcement: It prevents cracking and distributes stress in slabs, walls, and other concrete structures, enhancing durability and safety.
Architectural Uses: Mesh is employed in façade cladding and decorative elements, contributing to modern building aesthetics.
Safety and Security: It serves as a protective measure in window grills, security cages, and gates, offering enhanced security for buildings and their occupants.
Industrial Applications
In industrial spaces, mesh products serve critical roles, such as:
Aggregate Industry: Used for sizing and classifying materials in mining and processing.
Agriculture: Essential for grain screening, sorting, and fencing applications.
Filtration and Separation: Integral to filters, strainers, and separators for liquids and gases in industrial processes.
Infrastructure Uses
Wire mesh also supports infrastructure projects, including:
Urban Structures: It reinforces pavements, sidewalks, parking lots, bike paths, and sports facilities, improving durability and safety.
Transportation: Mesh is used in bridges, airport runways, and platforms to provide added strength and longevity.
Advantages in Project Implementation
This sturdy material also provides several practical advantages during project execution:
Easy Installation and Handling: Prefabricated sheets and rolls streamline logistics and placement, reducing complexity.
Reduced Labor and Operating Times: Quicker installation, when compared to traditional rebar, contributes to lower project costs.
Minimized Human Error: Factory-controlled production ensures consistent quality and reduces onsite variability.
Enhanced Safety Features: Wire mesh meets OSHA and industry safety standards for secure installations.
Environmental Considerations
Modern mesh production incorporates sustainable practices:
Use of Recycled Materials: Many manufacturers use recycled steel, supporting sustainability goals.
Energy Efficiency in Production: Advanced automation reduces energy consumption and production waste.
Longevity and Minimal Maintenance: Durable, corrosion-resistant mesh minimizes the need for replacement and maintenance, reducing environmental impact over time.
Wire Mesh: Beneficial Across Industries
Wire mesh’s beneficial properties and broad applications make it a vital material in construction, industrial spaces, and infrastructure. As technology advances, wire mesh will continue to evolve, offering even greater performance and environmental benefits for future projects.
—
Precision. Strength. Reliability. Get Top-Quality Steel Products With Peterson Company—Built to Last Since 1931. – Get A Quote Today!
